LevelDB 读写流程

@[TOC](leveldb 读写流程)
API
// A DB is a persistent ordered map from keys to values.
// A DB is safe for concurrent access from multiple threads without
// any external synchronization.
class LEVELDB_EXPORT DB {
public:
// Open the database with the specified "name".
// Stores a pointer to a heap-allocated database in *dbptr and returns
// OK on success.
// Stores nullptr in *dbptr and returns a non-OK status on error.
// Caller should delete *dbptr when it is no longer needed.
static Status Open(const Options& options, const std::string& name,
DB** dbptr);
...
// Set the database entry for "key" to "value". Returns OK on success,
// and a non-OK status on error.
// Note: consider setting options.sync = true.
virtual Status Put(const WriteOptions& options, const Slice& key,
const Slice& value) = 0;
// Remove the database entry (if any) for "key". Returns OK on
// success, and a non-OK status on error. It is not an error if "key"
// did not exist in the database.
// Note: consider setting options.sync = true.
virtual Status Delete(const WriteOptions& options, const Slice& key) = 0;
// Apply the specified updates to the database.
// Returns OK on success, non-OK on failure.
// Note: consider setting options.sync = true.
virtual Status Write(const WriteOptions& options, WriteBatch* updates) = 0;
// If the database contains an entry for "key" store the
// corresponding value in *value and return OK.
//
// If there is no entry for "key" leave *value unchanged and return
// a status for which Status::IsNotFound() returns true.
//
// May return some other Status on an error.
virtual Status Get(const ReadOptions& options, const Slice& key,
std::string* value) = 0;
// Return a heap-allocated iterator over the contents of the database.
// The result of NewIterator() is initially invalid (caller must
// call one of the Seek methods on the iterator before using it).
//
// Caller should delete the iterator when it is no longer needed.
// The returned iterator should be deleted before this db is deleted.
virtual Iterator* NewIterator(const ReadOptions& options) = 0;
// Return a handle to the current DB state. Iterators created with
// this handle will all observe a stable snapshot of the current DB
// state. The caller must call ReleaseSnapshot(result) when the
// snapshot is no longer needed.
virtual const Snapshot* GetSnapshot() = 0;
// Release a previously acquired snapshot. The caller must not
// use "snapshot" after this call.
virtual void ReleaseSnapshot(const Snapshot* snapshot) = 0;
...
};
class DBImpl : public DB {
public:
...
// Implementations of the DB interface
Status Put(const WriteOptions&, const Slice& key,
const Slice& value) override;
Status Delete(const WriteOptions&, const Slice& key) override;
Status Write(const WriteOptions& options, WriteBatch* updates) override;
Status Get(const ReadOptions& options, const Slice& key,
std::string* value) override;
Iterator* NewIterator(const ReadOptions&) override;
const Snapshot* GetSnapshot() override;
void ReleaseSnapshot(const Snapshot* snapshot) override;
...
}
Put & Delete
本质上最后都是用的 Write
put是写入kTypeValue标记的KV,delete是写入kTypeDeletion标记KV
Status DBImpl::Put(const WriteOptions& o, const Slice& key, const Slice& val) {
return DB::Put(o, key, val);
}
// Default implementations of convenience methods that subclasses of DB
// can call if they wish
Status DB::Put(const WriteOptions& opt, const Slice& key, const Slice& value) {
WriteBatch batch;
batch.Put(key, value);
return Write(opt, &batch);
}
Status DBImpl::Delete(const WriteOptions& options, const Slice& key) {
return DB::Delete(options, key);
}
Status DB::Delete(const WriteOptions& opt, const Slice& key) {
WriteBatch batch;
batch.Delete(key);
return Write(opt, &batch);
}
WriteBatch
WriteBatch 封装一个或者多个要写的数据
class LEVELDB_EXPORT WriteBatch {
public:
...
WriteBatch();
// Intentionally copyable.
WriteBatch(const WriteBatch&) = default;
WriteBatch& operator=(const WriteBatch&) = default;
~WriteBatch() { Clear(); }
// Store the mapping "key->value" in the database.
void Put(const Slice& key, const Slice& value);
// If the database contains a mapping for "key", erase it. Else do nothing.
void Delete(const Slice& key);
// WriteBatch header has an 8-byte sequence number followed by a 4-byte count.
static const size_t kHeader = 12;
// Clear all updates buffered in this batch.
void Clear() ;
...
private:
friend class WriteBatchInternal;
std::string rep_; // See comment in write_batch.cc for the format of rep_
};
WriteBatch 的 std::string rep_存储了所有通过 Put/Delete 接口传入的数据。
按照一定格式记录了:sequence (8 byte,该WriteBatch中第一条KV的seq), count (4 byte,该WriteBatch总共包含多少条KV), [操作类型(Put or Delete),key/value的长度及key/value本身]…

Write
外部调写的接口是可以并发的,但leveldb内部保证了写是单线程无并发的
 WriterBatch封装了数据,DBImpl::Writer则封装了WriteBatch 和 mutex cond 同步原语,以及是否sync。
WriterBatch封装了数据,DBImpl::Writer则封装了WriteBatch 和 mutex cond 同步原语,以及是否sync。
// Information kept for every waiting writer
struct DBImpl::Writer {
Status status;
WriteBatch* batch;
bool sync;
bool done;
port::CondVar cv;
explicit Writer(port::Mutex* mu) : cv(mu) { }
};
先初始化 Writer
Status DBImpl::Write(const WriteOptions& options, WriteBatch* updates) {
Writer w(&mutex_);
w.batch = updates;
w.sync = options.sync;
w.done = false;
把 w 放进 writers_ 队列,只要自己还没有被写入(一定还在队列里),且队列前面还有其他 Writer,这个线程就等着。
MutexLock l(&mutex_);
writers_.push_back(&w);
while (!w.done && &w != writers_.front()) {
w.cv.Wait();
}
if (w.done) { // 自己已经被写入(一定已经被弹出队列了),可以返回结果了
return w.status;
}
走到这里,这时候这个线程的 Writer w 已经是队列的第一个了,且拿到了mutex_
// May temporarily unlock and wait.
Status status = MakeRoomForWrite(updates == nullptr);
BuildBatchGroup 的作用是聚合队列中多个线程的 WriteBatch 写请求到一个 WriteBatch,当然聚合后的 size 是有上限的,不能过大。
- last_writer = &w
- 向后遍历 writers_ 队列,逐渐递增 batch
- 更新 last_writer, 相当于记录哪些 writer 中的 batch 已经被聚合了,后面不用再写这些 writer。
uint64_t last_sequence = versions_->LastSequence(); // 获取 last seq
Writer* last_writer = &w;
if (status.ok() && updates != nullptr) { // nullptr batch is for compactions
WriteBatch* write_batch = BuildBatchGroup(&last_writer);
设置这个聚合过后的write_batch的seq,并且last_sequence += write_batch的entry数量
WriteBatchInternal::SetSequence(write_batch, last_sequence + 1);
last_sequence += WriteBatchInternal::Count(write_batch);
先将write_batch的rep_这一整个string(WriteBatchInternal::Contents(write_batch))作为一条record写入log 再将这个write_batch的每一条entry一条一条的写入mem table,且每一条entry的seq递增(WriteBatchInternal::InsertInto(write_batch, mem_))
// Add to log and apply to memtable. We can release the lock
// during this phase since &w is currently responsible for logging
// and protects against concurrent loggers and concurrent writes
// into mem_.
{
mutex_.Unlock();
status = log_->AddRecord(WriteBatchInternal::Contents(write_batch));
bool sync_error = false;
if (status.ok() && options.sync) { // sync
status = logfile_->Sync();
if (!status.ok()) {
sync_error = true;
}
}
if (status.ok()) {
status = WriteBatchInternal::InsertInto(write_batch, mem_);
}
mutex_.Lock();
if (sync_error) {
// The state of the log file is indeterminate: the log record we
// just added may or may not show up when the DB is re-opened.
// So we force the DB into a mode where all future writes fail.
RecordBackgroundError(status);
}
}
if (write_batch == tmp_batch_) tmp_batch_->Clear();
更新VersionSet::last_sequence_
versions_->SetLastSequence(last_sequence);
}
因为last_writer和在它之前的writer都已经被BuildBatchGroup聚合到一起写入了,所以要现将这些writer弹出,将它们所属的线程唤醒,最后唤醒剩余队列中的第一个writer
while (true) {
Writer* ready = writers_.front();
writers_.pop_front();
if (ready != &w) { // 不用唤醒 w,因为现在正在执行的就是 w 线程
ready->status = status;
ready->done = true;
ready->cv.Signal();
}
if (ready == last_writer) break;
}
// Notify new head of write queue
if (!writers_.empty()) {
writers_.front()->cv.Signal();
}
return status;
}
批量写入一个典型问题就是一致性,例如这么调用:
leveldb::WriteBatch batch;
batch.Put("language", "Golang");
batch.Put("company", "Google");
batch.Put("language", "Java");
batch.Put("company", "FaceBook");
db->Write(write_option, &batch);
我们肯定不希望读到company -> Google,language -> Golang这两个中间结果。因为WriteBatch这个类没有去重功能,所以以上4条数据都会写入mem,但是每条的seq不同,且是单调递增的。 但是为什么我们读不到中间结果呢,因为写入时,每条的seq递增的更新到 memtable,但是只把最后一个seq记录到VersionSet::last_sequence_:
uint64_t last_sequence = versions_->LastSequence();//本次写入的SequenceNumber
...
WriteBatchInternal::SetSequence(write_batch, last_sequence + 1);
last_sequence += WriteBatchInternal::Count(write_batch);
...
versions_->SetLastSequence(last_sequence);
对于Get操作(参考本文 Get 一节),首先需要通过versions_->LastSequence()获取一个read_seq,read_seq 只有两种可能:
(1) <= last_sequence seek的时候,这4个值我都看不到 (2) >= last_sequence + Count(write_batch) seek的时候一定先看到last_sequence+3或+4,因此读取时不会观察到中间状态。
Snapshot
class DBImpl : public DB {
private:
SnapshotList snapshots_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
}
const Snapshot* DBImpl::GetSnapshot() {
MutexLock l(&mutex_);
return snapshots_.New(versions_->LastSequence());
}
void DBImpl::ReleaseSnapshot(const Snapshot* snapshot) {
MutexLock l(&mutex_);
snapshots_.Delete(static_cast<const SnapshotImpl*>(snapshot));
}
SnapshotList 是一个双链表。
 一个SnapshotImpl就是SnapshotImpl链表中的一个entry;entry记录了业务请求获取snapshot时leveldb的versions_->LastSequence()。业务读snapshot的时候会把这个entry中记录的seq作为read_seq。
一个SnapshotImpl就是SnapshotImpl链表中的一个entry;entry记录了业务请求获取snapshot时leveldb的versions_->LastSequence()。业务读snapshot的时候会把这个entry中记录的seq作为read_seq。
class LEVELDB_EXPORT Snapshot {
protected:
virtual ~Snapshot();
};
// Snapshots are kept in a doubly-linked list in the DB.
// Each SnapshotImpl corresponds to a particular sequence number.
class SnapshotImpl : public Snapshot {
public:
SnapshotImpl(SequenceNumber sequence_number)
: sequence_number_(sequence_number) {}
SequenceNumber sequence_number() const { return sequence_number_; }
private:
friend class SnapshotList;
// SnapshotImpl is kept in a doubly-linked circular list. The SnapshotList
// implementation operates on the next/previous fields direcly.
SnapshotImpl* prev_;
SnapshotImpl* next_;
const SequenceNumber sequence_number_;
};
class SnapshotList {
public:
SnapshotList() : head_(0) {
head_.prev_ = &head_;
head_.next_ = &head_;
}
bool empty() const { return head_.next_ == &head_; }
SnapshotImpl* oldest() const {
assert(!empty());
return head_.next_;
}
SnapshotImpl* newest() const {
assert(!empty());
return head_.prev_;
}
// Creates a SnapshotImpl and appends it to the end of the list.
SnapshotImpl* New(SequenceNumber sequence_number);
// Removes a SnapshotImpl from this list.
//
// The snapshot must have been created by calling New() on this list.
//
// The snapshot pointer should not be const, because its memory is
// deallocated. However, that would force us to change DB::ReleaseSnapshot(),
// which is in the API, and currently takes a const Snapshot.
void Delete(const SnapshotImpl* snapshot);
private:
// Dummy head of doubly-linked list of snapshots
SnapshotImpl head_;
};
snapshot对major compaction的影响
一个snapshot就是snapshot链表中的一个entry;entry记录了业务请求获取snapshot时leveldb的versions_->LastSequence()。在leveldb做major compaction的时候,会去查看这个snapshot链表的oldest即最小的seq,会确保db中seq大于seq的kv不会在major compaction中被drop掉(小于等于该seq中的最大的seq也不会被drop),这样持有snapshot的业务才能看得见他们应该看见的kv。
个人认为如果有大量业务对db做了大量不同时期的snapshot,这会很影响major compaction。可不可以采用一种新的snapshot策略:一个snapshot中记录的不是versions_->LastSequence(),而是记录获取snapshot时刻的db中current version(versions_->current()->Ref())。业务读这个snapshot的时候就只从这个version的sst文件里读;只要我这个snapshot没release,那这个version(这些sst文件)就不能删。这样做major compaction的时候就不需要考虑之前的问题了。但是这就引入了另一个问题,我mem table中的kv怎么办呢?因为snapshot不光包括获取snapshot时刻db中current version的所有sst文件,还包括那一时刻的mem table,但是mem table的内容是可变的,可能做完snapshot过了一会这个mem table就被minor compact成一个sst了,但是这个sst没有被记录在刚才那个snapshot entry中(好像只要把这个sst加到刚才那个snapshot entry中保存的version的sst文件信息中去,问题就解决了)。
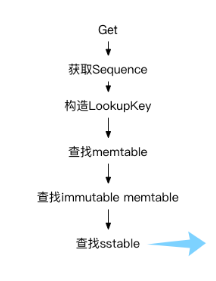
Get
整体流程
MutexLock l(&mutex_)
- 获取seq(如果指定某个snapshot则为snapshot中保存的seq,否则为(versions_->LastSequence())
- versions_->current()->Ref(); mem->Ref(); imm->Ref()
mutex_.Unlock()
- LookupKey lkey(key, snapshot),将刚刚获取的seq和业务要查找的user_key组成一个LookupKey
- mem->Get
- imm->Get
- current->Get,同时进行采样探测
mutex_.Lock()
- MaybeScheduleCompaction()
- versions_->current()->UnRef(); mem->UnRef(); imm->UnRef()
Status DBImpl::Get(const ReadOptions& options, const Slice& key,
std::string* value) {
Status s;
MutexLock l(&mutex_);
SequenceNumber snapshot;
if (options.snapshot != nullptr) {
snapshot =
static_cast<const SnapshotImpl*>(options.snapshot)->sequence_number();
} else {
snapshot = versions_->LastSequence();
}
MemTable* mem = mem_;
MemTable* imm = imm_;
mem->Ref();
if (imm != nullptr) imm->Ref();
Version* current = versions_->current();
current->Ref();
bool have_stat_update = false;
Version::GetStats stats;
// Unlock while reading from files and memtables
{
mutex_.Unlock();
// First look in the memtable, then in the immutable memtable (if any).
LookupKey lkey(key, snapshot);
if (mem->Get(lkey, value, &s)) {
// Done
} else if (imm != nullptr && imm->Get(lkey, value, &s)) {
// Done
} else {
s = current->Get(options, lkey, value, &stats);
have_stat_update = true;
}
mutex_.Lock();
}
if (have_stat_update && current->UpdateStats(stats)) {
MaybeScheduleCompaction();
}
mem->Unref();
if (imm != nullptr) imm->Unref();
current->Unref();
return s;
}
MemTable::Get
Version::Get
Status Version::Get(const ReadOptions& options, const LookupKey& k,
std::string* value, GetStats* stats) {
// 初始化采样探测信息
stats->seek_file = nullptr;
stats->seek_file_level = -1;
struct State {
Saver saver;
GetStats* stats;
const ReadOptions* options;
Slice ikey;
FileMetaData* last_file_read;
int last_file_read_level;
VersionSet* vset;
Status s;
bool found;
static bool Match(void* arg, int level, FileMetaData* f);
};
// 初始化state信息
State state;
state.found = false;
state.stats = stats;
state.last_file_read = nullptr;
state.last_file_read_level = -1;
state.options = &options;
state.ikey = k.internal_key();
state.vset = vset_;
state.saver.state = kNotFound;
state.saver.ucmp = vset_->icmp_.user_comparator();
state.saver.user_key = k.user_key();
state.saver.value = value;
ForEachOverlapping(state.saver.user_key, state.ikey, &state, &State::Match);
return state.found ? state.s : Status::NotFound(Slice());
}
Version::ForEachOverlapping
对所有和user_key存在overlap的sst文件,依次调用 bool (func)(void, int, FileMetaData*),如果函数返回false说明找到了,或者查找过程中出现错误,则不再继续查找。返回true说明需要继续查找下一个可能的sst。

- 因为level0的sst存在overlap,所以level0层的所有和user_key有overlap的sst必须按照由新到旧的顺序挨个找一遍
- 其他level的sst不存在overlap,所以每一层只需要找一个sst(FindFile这个函数用二分的方法选择出每一层该查找的sst)
// Call func(arg, level, f) for every file that overlaps user_key in
// order from newest to oldest. If an invocation of func returns
// false, makes no more calls.
//
// REQUIRES: user portion of internal_key == user_key.
void Version::ForEachOverlapping(Slice user_key, Slice internal_key, void* arg,
bool (*func)(void*, int, FileMetaData*)) {
const Comparator* ucmp = vset_->icmp_.user_comparator();
// Search level-0 in order from newest to oldest.
// 因为level0的sst存在overlap,
// 所以level0层的所有和user_key有overlap的sst必须按照由新到旧的顺序挨个找一遍
std::vector<FileMetaData*> tmp;
tmp.reserve(files_[0].size());
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < files_[0].size(); i++) {
FileMetaData* f = files_[0][i];
if (ucmp->Compare(user_key, f->smallest.user_key()) >= 0 &&
ucmp->Compare(user_key, f->largest.user_key()) <= 0) {
tmp.push_back(f);
}
}
if (!tmp.empty()) {
// 通过sst文件的file number来判断文件的新旧,按从新到旧排列
std::sort(tmp.begin(), tmp.end(), NewestFirst);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < tmp.size(); i++) {
if (!(*func)(arg, 0, tmp[i])) {
return;
}
}
}
// Search other levels.
// 其他level的sst不存在overlap,
// 所以每一层只需要找一个sst(FindFile这个函数用二分的方法选择出每一层该查找的sst)
for (int level = 1; level < config::kNumLevels; level++) {
size_t num_files = files_[level].size();
if (num_files == 0) continue;
// Binary search to find earliest index whose largest key >= internal_key.
uint32_t index = FindFile(vset_->icmp_, files_[level], internal_key);
if (index < num_files) {
FileMetaData* f = files_[level][index];
if (ucmp->Compare(user_key, f->smallest.user_key()) < 0) {
// All of "f" is past any data for user_key
} else {
if (!(*func)(arg, level, f)) {
return;
}
}
}
}
}
Version::Get::State::Match
查找某个sst文件,返回false说明找到了,或者查找过程中出现错误,则不再继续查找。返回true说明需要继续查找下一个可能的sst。
static bool Version::Get::State::Match(void* arg, int level, FileMetaData* f) {
State* state = reinterpret_cast<State*>(arg);
// 本次Get操作访问的第一个sstable文件如果没找到key
// 采样探测会记录这个第一个访问的sst
if (state->stats->seek_file == nullptr &&
state->last_file_read != nullptr) {
// We have had more than one seek for this read. Charge the 1st file.
state->stats->seek_file = state->last_file_read;
state->stats->seek_file_level = state->last_file_read_level;
}
state->last_file_read = f;
state->last_file_read_level = level;
state->s = state->vset->table_cache_->Get(*state->options, f->number,
f->file_size, state->ikey,
&state->saver, SaveValue);
if (!state->s.ok()) {
state->found = true;
return false;
}
switch (state->saver.state) {
case kNotFound:
return true; // Keep searching in other files
case kFound:
state->found = true;
return false;
case kDeleted:
return false;
case kCorrupt:
state->s =
Status::Corruption("corrupted key for ", state->saver.user_key);
state->found = true;
return false;
}
// Not reached. Added to avoid false compilation warnings of
// "control reaches end of non-void function".
return false;
}
TableCache::Get
SaveValue
在Table::InternalGet会同步调用参数handle_result也就是SaveValue,用来判断block_iter->Seek(k)的结果(参数ikey)是不是我们想要Get的user_key。如果是,且kTypeValue则说明该次业务的get操作找到了对应的key
struct Saver {
SaverState state;
const Comparator* ucmp;
Slice user_key;
std::string* value;
};
static void SaveValue(void* arg, const Slice& ikey, const Slice& v) {
Saver* s = reinterpret_cast<Saver*>(arg);
ParsedInternalKey parsed_key;
if (!ParseInternalKey(ikey, &parsed_key)) {
s->state = kCorrupt;
} else {
if (s->ucmp->Compare(parsed_key.user_key, s->user_key) == 0) { // user_key match
s->state = (parsed_key.type == kTypeValue) ? kFound : kDeleted;
if (s->state == kFound) {
s->value->assign(v.data(), v.size());
}
}
}
}
NewIterator
Iterator* DBImpl::NewIterator(const ReadOptions& options) {
SequenceNumber latest_snapshot;
uint32_t seed;
Iterator* iter = NewInternalIterator(options, &latest_snapshot, &seed);
return NewDBIterator(this, user_comparator(), iter, (options.snapshot != nullptr ? static_cast<const SnapshotImpl*>(options.snapshot)->sequence_number(): latest_snapshot), seed);
}

NewInternalIterator
NewInternalIterator实际上创建了一个MergingIterator
需要merge mem的iterator
需要merge imm的iterator
需要分别merge level 0所有的sst的iterator
需要分别给Level >= 1的每一层创建一个ConcatenatingIterator,并分别merge它们
MutexLock l(&mutex_)
- 获取seq(为versions_->LastSequence())
- versions_->current()->Ref(); mem->Ref(); imm->Ref()
- 将多个子iterator合并生成MergingIterator
mutex_.Unlock()
Iterator* DBImpl::NewInternalIterator(const ReadOptions& options,
SequenceNumber* latest_snapshot,
uint32_t* seed) {
mutex_.Lock();
*latest_snapshot = versions_->LastSequence();
// Collect together all needed child iterators
std::vector<Iterator*> list;
list.push_back(mem_->NewIterator()); // 需要merge mem_ iterator
mem_->Ref();
if (imm_ != nullptr) {
list.push_back(imm_->NewIterator()); // 需要merge imm_ iterator
imm_->Ref();
}
// 需要分别merge level 0所有的sst的iterator
// 需要分别给Level >= 1的每一层创建一个ConcatenatingIterator,并分别merge它们
versions_->current()->AddIterators(options, &list);
Iterator* internal_iter = // 创建MergingIterator
NewMergingIterator(&internal_comparator_, &list[0], list.size());
versions_->current()->Ref();
IterState* cleanup = new IterState(&mutex_, mem_, imm_, versions_->current());
internal_iter->RegisterCleanup(CleanupIteratorState, cleanup, nullptr);
*seed = ++seed_;
mutex_.Unlock();
return internal_iter;
}
// Append to *iters a sequence of iterators that will
// yield the contents of this Version when merged together.
// REQUIRES: This version has been saved (see VersionSet::SaveTo)
void Version::AddIterators(const ReadOptions& options,
std::vector<Iterator*>* iters) {
// Merge all level zero files together since they may overlap
// 需要merge level0所有的sst的iterator
for (size_t i = 0; i < files_[0].size(); i++) {
iters->push_back(vset_->table_cache_->NewIterator(
options, files_[0][i]->number, files_[0][i]->file_size));
}
// For levels > 0, we can use a concatenating iterator that sequentially
// walks through the non-overlapping files in the level, opening them
// lazily.
// 需要给每一层创建一个ConcatenatingIterator
// 然后merge他们
for (int level = 1; level < config::kNumLevels; level++) {
if (!files_[level].empty()) {
iters->push_back(NewConcatenatingIterator(options, level));
}
}
}
MergingIterator
MergingIterator可以实现多个有序数据集合的归并操作。MergingIterator 内部有多个有序块(每个块都存储的是internal_key),这些有序块分别有一个 iterator(children_[i]) 来遍历,对MergingIterator的遍历(不断掉Next())会有序的遍历其child iterator中的每个元素。
 如果从头开始不断的调用Next(),则首先通过 iter2 访问块 2 的 0, 接着通过 iter1 访问块 1 的 1,iter2 - 块 2-2, iter3 - 块 3-3….
如果从头开始不断的调用Next(),则首先通过 iter2 访问块 2 的 0, 接着通过 iter1 访问块 1 的 1,iter2 - 块 2-2, iter3 - 块 3-3….
// Return an iterator that provided the union of the data in
// children[0,n-1]. Takes ownership of the child iterators and
// will delete them when the result iterator is deleted.
//
// The result does no duplicate suppression. I.e., if a particular
// key is present in K child iterators, it will be yielded K times.
//
// REQUIRES: n >= 0
Iterator* NewMergingIterator(const Comparator* comparator, Iterator** children, int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
if (n == 0) {
return NewEmptyIterator();
} else if (n == 1) {
return children[0];
} else {
return new MergingIterator(comparator, children, n);
}
}
成员变量和构造函数
class MergingIterator : public Iterator {
public:
MergingIterator(const Comparator* comparator, Iterator** children, int n)
: comparator_(comparator),
children_(new IteratorWrapper[n]),
n_(n),
current_(nullptr),
direction_(kForward) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
children_[i].Set(children[i]);
}
}
~MergingIterator() override { delete[] children_; }
...
private:
// Which direction is the iterator moving?
enum Direction { kForward, kReverse };
...
// We might want to use a heap in case there are lots of children.
// For now we use a simple array since we expect a very small number
// of children in leveldb.
const Comparator* comparator_;
IteratorWrapper* children_; // children iter 数组
int n_; // n 个 children iter
IteratorWrapper* current_;
Direction direction_;
};
部分的接口实现
// 先将所有 child iterator 各自 SeekToFirst
// 然后再 FindSmallest
void MergingIterator::SeekToFirst() override {
for (int i = 0; i < n_; i++) {
children_[i].SeekToFirst();
}
FindSmallest();
direction_ = kForward;
}
// 遍历所有 iterator 中找到目前 key 最小的那个, current_指向具有最小 key 的 iterator。
void MergingIterator::FindSmallest() {
IteratorWrapper* smallest = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < n_; i++) {
IteratorWrapper* child = &children_[i];
if (child->Valid()) {
if (smallest == nullptr) {
smallest = child;
} else if (comparator_->Compare(child->key(), smallest->key()) < 0) {
smallest = child;
}
}
}
current_ = smallest;
}
bool MergingIterator::Valid() const override {
return (current_ != nullptr);
}
Slice MergingIterator::key() const override {
assert(Valid());
return current_->key();
}
// 先将所有 child iterator 各自 Seek
// 然后再 FindSmallest
void MergingIterator::Seek(const Slice& target) override {
for (int i = 0; i < n_; i++) {
children_[i].Seek(target);
}
FindSmallest();
direction_ = kForward;
}
// 找到 MergeingIterator 中大于当前 key() 的所有 key 中最小的一个
void MergingIterator::Next() override {
assert(Valid());
// Ensure that all children are positioned after key().
// If we are moving in the forward direction, it is already
// true for all of the non-current_ children since current_ is
// the smallest child and key() == current_->key(). Otherwise,
// we explicitly position the non-current_ children.
if (direction_ != kForward) {
for (int i = 0; i < n_; i++) {
IteratorWrapper* child = &children_[i];
if (child != current_) {
child->Seek(key());
if (child->Valid() &&
comparator_->Compare(key(), child->key()) == 0) {
child->Next();
}
}
}
direction_ = kForward;
}
current_->Next();
FindSmallest();
}
ConcatenatingIterator
ConcatenatingIterator实际上是一个由 LevelFileNumIterator(作为index_iter_)和 TableIterator 作为(data_iter_)组成的 TwoLevelIterator
Iterator* Version::NewConcatenatingIterator(const ReadOptions& options, int level) const {
return NewTwoLevelIterator(
new LevelFileNumIterator(vset_->icmp_, &files_[level]), &GetFileIterator,
vset_->table_cache_, options);
}
LevelFileNumIterator
其中Level1层和之上的sst文件由于相互之间没有交集且有序,可以利用FileMetaData中的最大或最小的Key来进行二分查找。LevelFileNumIterator就是利用这个特点实现的对sst文件元信息(file_number + file_size)进行遍历的Iterator。LevelFileNumIterator中的每对 key-value 记录了当前文件最大key到文件元信息的映射关系。
// An internal iterator. For a given version/level pair, yields
// information about the files in the level. For a given entry, key()
// is the largest key that occurs in the file, and value() is an
// 16-byte value containing the file number and file size, both
// encoded using EncodeFixed64.
class Version::LevelFileNumIterator : public Iterator {
public:
LevelFileNumIterator(const InternalKeyComparator& icmp,
const std::vector<FileMetaData*>* flist)
: icmp_(icmp), flist_(flist), index_(flist->size()) { // Marks as invalid
}
bool Valid() const override { return index_ < flist_->size(); }
// 在 flist_ 中找到可能包含 target 的sst
void Seek(const Slice& target) override {
index_ = FindFile(icmp_, *flist_, target);
}
void SeekToFirst() override { index_ = 0; }
void SeekToLast();
void Next() override {
assert(Valid());
index_++;
}
void Prev();
// For a given entry, key()
// is the largest key that occurs in the file
Slice key() const override {
assert(Valid());
return (*flist_)[index_]->largest.Encode();
}
// value() is an
// 16-byte value containing the file number and file size, both
// encoded using EncodeFixed64.
Slice value() const override {
assert(Valid());
EncodeFixed64(value_buf_, (*flist_)[index_]->number);
EncodeFixed64(value_buf_ + 8, (*flist_)[index_]->file_size);
return Slice(value_buf_, sizeof(value_buf_));
}
Status status() const override { return Status::OK(); }
private:
const InternalKeyComparator icmp_;
const std::vector<FileMetaData*>* const flist_; // f存放的是某一层所有 sst 的 FileMetaData
uint32_t index_; // 当前指向的 sst 的 FileMetaData
// Backing store for value(). Holds the file number and size.
mutable char value_buf_[16];
};
// 用二分查找
// 查找 FileMetaData::largest 大于 key 的所有文件中最小的一个
int FindFile(const InternalKeyComparator& icmp,
const std::vector<FileMetaData*>& files, const Slice& key) {
uint32_t left = 0;
uint32_t right = files.size();
while (left < right) {
uint32_t mid = (left + right) / 2;
const FileMetaData* f = files[mid];
if (icmp.InternalKeyComparator::Compare(f->largest.Encode(), key) < 0) {
// Key at "mid.largest" is < "target". Therefore all
// files at or before "mid" are uninteresting.
left = mid + 1;
} else {
// Key at "mid.largest" is >= "target". Therefore all files
// after "mid" are uninteresting.
right = mid;
}
}
return right;
}
GetFileIterator
负责把 LevelFileNumIterator::value() 的输出,转换成 TableIterator
static Iterator* GetFileIterator(void* arg, const ReadOptions& options,
const Slice& file_value) {
TableCache* cache = reinterpret_cast<TableCache*>(arg);
if (file_value.size() != 16) {
return NewErrorIterator(
Status::Corruption("FileReader invoked with unexpected value"));
} else {
return cache->NewIterator(options, DecodeFixed64(file_value.data()),
DecodeFixed64(file_value.data() + 8));
}
}
TableCache::NewIterator
DBIter
DBIter 是最最顶层的Iterator,封装了DBImpl::NewInternalIterator 输出的 MergingIterator
Iterator* DBImpl::NewIterator(const ReadOptions& options) {
SequenceNumber latest_snapshot;
uint32_t seed;
Iterator* iter = NewInternalIterator(options, &latest_snapshot, &seed);
return NewDBIterator(this, user_comparator(), iter, (options.snapshot != nullptr ? static_cast<const SnapshotImpl*>(options.snapshot)->sequence_number(): latest_snapshot), seed);
}
Iterator* NewDBIterator(DBImpl* db, const Comparator* user_key_comparator, Iterator* internal_iter, SequenceNumber sequence, uint32_t seed) {
return new DBIter(db, user_key_comparator, internal_iter, sequence, seed);
}
Leveldb 数据库的 MemTable 和 sstable 文件的存储格式都是 InternalKey (userkey, seq, type) => uservalue。所以之前所述的 iterator 都是输出 InternalKey => uservalue的映射。 然而用户只会关心 userkey => uservalue 的映射,DBIter 只会把最新的userkey (seq 小于等于 读sequence 中最大的就是最新的,相同 userkey 的老记录(seq 较小的)会被DBIter skip掉,不会让用户看到)的一条记录展现给用户。
成员变量和构造函数
// Memtables and sstables that make the DB representation contain
// (userkey,seq,type) => uservalue entries. DBIter
// combines multiple entries for the same userkey found in the DB
// representation into a single entry while accounting for sequence
// numbers, deletion markers, overwrites, etc.
class DBIter : public Iterator {
public:
// Which direction is the iterator currently moving?
// (1) When moving forward, the internal iterator is positioned at
// the exact entry that yields this->key(), this->value()
// (2) When moving backwards, the internal iterator is positioned
// just before all entries whose user key == this->key().
enum Direction { kForward, kReverse };
DBIter(DBImpl* db, const Comparator* cmp, Iterator* iter, SequenceNumber s,
uint32_t seed)
: db_(db),
user_comparator_(cmp),
iter_(iter),
sequence_(s),
direction_(kForward),
valid_(false),
rnd_(seed),
bytes_until_read_sampling_(RandomCompactionPeriod()) {}
...
private:
...
DBImpl* db_;
const Comparator* const user_comparator_;
Iterator* const iter_; // 是一个MergingIterator
SequenceNumber const sequence_; // DBIter只应该访问到比sequence_小的kv
Status status_;
std::string saved_key_; // == current key when direction_==kReverse
std::string saved_value_; // == current raw value when direction_==kReverse
Direction direction_;
bool valid_;
Random rnd_;
size_t bytes_until_read_sampling_;
};
iter_是由 NewInternalIterator 创建的一个 MergingIterator,因为 iter_遍历的是leveldb的每一条记录。它是以 InternalKey (userkey, seq, type) 为遍历粒度的,只要 InternalKey 中任意一个组成元素不同,MergingIterator 就认为他们是不同的 kv 对。 而 DBIter 是以 userkey 为遍历粒度的,不同的InternalKey,只要其中的 userkey 相同(seq不同),那么 DBIter 就认为他们是一条记录,seq 越大代表该记录越新。每次迭代将跳到下一个不同 userkey 的记录,且 DBIter 在遍历一个 InternalKey 时仅会检索 InternalKey->seq 小于 DBIter 创建时所初始化的 seq 号。举个例子:
 上面表示了 6 个 InternalKey,冒号前为 user_key, 冒号后为序列号。现假设创建 DBIter 时,所初始化的 seq 为 2. 则 DBIter 在从前往后遍历时,将会直接跳过 key1:6,key1:5,key1:4 和 key2:3. 只会从 key2:2 开始遍历。
上面表示了 6 个 InternalKey,冒号前为 user_key, 冒号后为序列号。现假设创建 DBIter 时,所初始化的 seq 为 2. 则 DBIter 在从前往后遍历时,将会直接跳过 key1:6,key1:5,key1:4 和 key2:3. 只会从 key2:2 开始遍历。
部分的接口实现
void DBIter::SeekToFirst() {
direction_ = kForward;
ClearSavedValue();
iter_->SeekToFirst(); // MergingIterator::SeekToFirst()
if (iter_->Valid()) {
FindNextUserEntry(false, &saved_key_ /* temporary storage */);
} else {
valid_ = false;
}
}
DBIter::FindNextUserEntry 的作用是找到下一个(按user_key排序),用户应该看到的 user_key
void DBIter::FindNextUserEntry(bool skipping, std::string* skip) {
// skip 是上一个用户应该看到的 user_key
// skipping 代表如果我继续 iter_->Next(),
// 碰到了一个 internal_key 其 user_key 和 skip 一样。我要不要跳过
// Loop until we hit an acceptable entry to yield
assert(iter_->Valid());
assert(direction_ == kForward);
do {
ParsedInternalKey ikey;
// 将 iter_->key() 解析为 ikey,且 ikey.sequence <= sequence_ 说明用户是可以看得到的
if (ParseKey(&ikey) && ikey.sequence <= sequence_) {
switch (ikey.type) {
case kTypeDeletion: // 是个墓碑,用户就不应该看见
// Arrange to skip all upcoming entries for this key since
// they are hidden by this deletion.
SaveKey(ikey.user_key, skip); // 将 skip reset 为 ikey.user_key
skipping = true;
break;
case kTypeValue:
if (skipping &&
user_comparator_->Compare(ikey.user_key, *skip) <= 0) {
// ikey.user_key, *skip 是一样的,且 skipping,所以跳过
// Entry hidden
} else {
// 找到了
valid_ = true;
saved_key_.clear();
return;
}
break;
}
}
iter_->Next(); // 继续 iter_->Next()
} while (iter_->Valid());
saved_key_.clear();
valid_ = false;
}
Slice key() const override {
assert(valid_);
return (direction_ == kForward) ? ExtractUserKey(iter_->key()) : saved_key_;
}
void DBIter::Seek(const Slice& target) {
direction_ = kForward;
ClearSavedValue();
saved_key_.clear();
AppendInternalKey(&saved_key_,
ParsedInternalKey(target, sequence_, kValueTypeForSeek));
iter_->Seek(saved_key_);
if (iter_->Valid()) {
FindNextUserEntry(false, &saved_key_ /* temporary storage */);
} else {
valid_ = false;
}
}
void DBIter::Next() {
assert(valid_);
if (direction_ == kReverse) { // Switch directions?
...
} else {
// Store in saved_key_ the current key so we skip it below.
SaveKey(ExtractUserKey(iter_->key()), &saved_key_);
// iter_ is pointing to current key. We can now safely move to the next to
// avoid checking current key.
iter_->Next();
if (!iter_->Valid()) {
valid_ = false;
saved_key_.clear();
return;
}
}
FindNextUserEntry(true, &saved_key_);
}
参考
https://izualzhy.cn/leveldb-write-read https://www.ravenxrz.ink/archives/1ba074b9.html https://catkang.github.io/2017/02/12/leveldb-iterator.html